Coronary Angioplasty Treatment
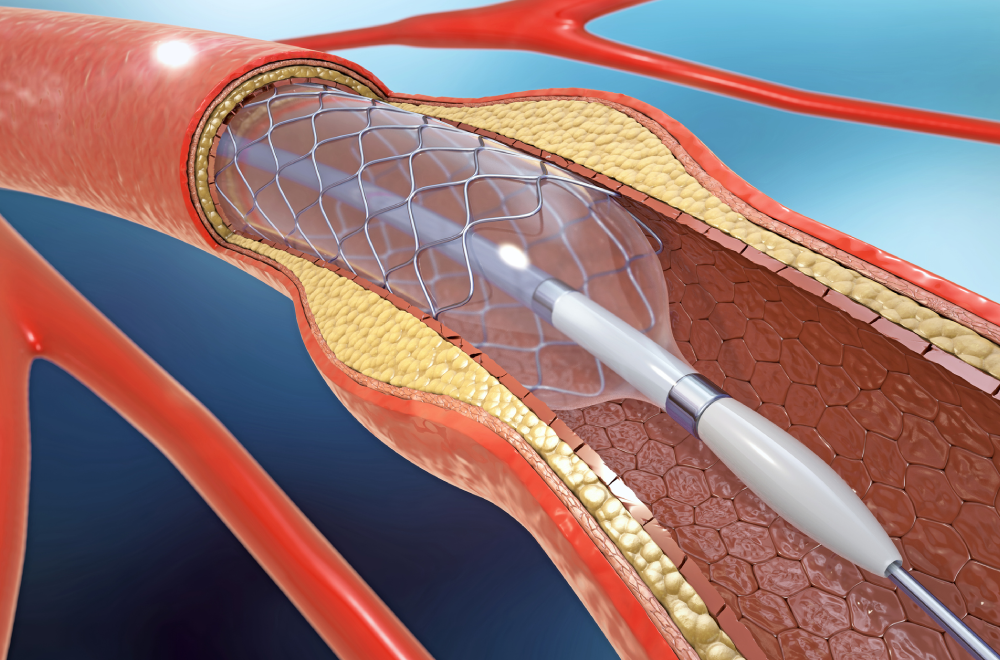
Coronary angioplasty (AN-jee-o-plas-tee) is a procedure to open clogged blood vessels of the heart. Coronary angioplasty treats vessels, called coronary arteries, which deliver blood to heart muscles. A tiny balloon on a narrow tube, called a catheter, is used to widen a clogged artery and improve blood flow.
Angioplasty is often followed by the placement of a small wire mesh tube called a stent. The stent helps prop the artery open and decreases the chance of the artery narrowing again. Most stents are coated with medicine that helps keep the artery open.
Angioplasty and stent placement may be a planned procedure to improve blood flow to the heart muscles. The procedure also may be used as emergency treatment for a heart attack.
Get expert Dr. Sai Ravi Shanker,Coronary Angioplasty Treatment in Ameerpet, Hyderabad with the best heart specialists, Quick diagnosis, and advanced care.
Symptoms
Symptoms of coronary angioplasty with stent placement may include:
-
Re-narrowing of the artery
Re-narrowing of the artery, also called re-stenosis, is more likely to occur if no stent is used. If the stent is coated with a medicine, there is even less risk of narrowing.
-
Blood clots
Blood clots can form within stents. These clots can close the artery, causing a heart attack. Medicines can help reduce the risk of blood clots.
-
Bleeding or infection
During the procedure, a catheter is inserted into a blood vessel, usually in the arm or leg. Bleeding, bruising, or infection may occur where the catheter was inserted.
Other rare risks of angioplasty include:
-
Heart attack
Heart attacks that cause severe tissue damage or death are rare.
-
Coronary artery damage
The coronary artery may be torn or ruptured during coronary angioplasty and stenting. These complications may require emergency open-heart surgery.
-
Kidney injury
The risk is higher when other conditions already affect how well the kidneys work.
-
Stroke
During angioplasty, a piece of fatty plaque can break loose, travel to the brain, and block blood flow. A stroke is an extremely rare complication of coronary angioplasty. Blood thinners are used during the procedure to reduce the risk.
-
Irregular heartbeats
During the procedure, the heart may beat too fast or too slow. These heart rhythm problems may need to be treated with medicine or a temporary pacemaker.
After getting a stent, you may need to take medicines to prevent blood clots. Your doctor may recommend taking aspirin with another medicine, such as clopidogrel (Plavi), ticagrelor (Brilinta) or prasugrel (Effient). Aspirin recommendations vary. Check with your healthcare team before starting aspirin.
Explore More : Primary Coronary Angioplasty
